The content of the article:
- Is it possible to diagnose and fix problems yourself
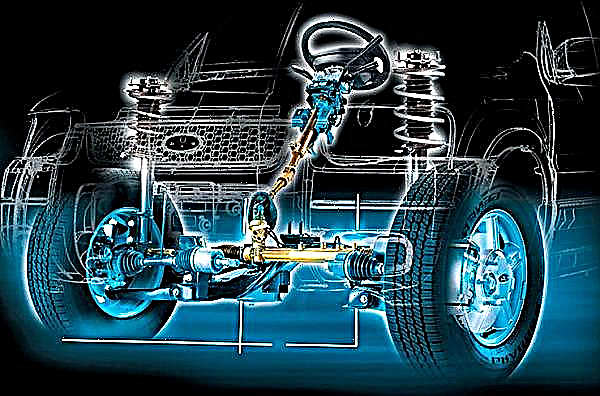
- Steering - purpose and design
- Car suspension
- The most common problems of switchgear and suspension, their identification and elimination
- Symptoms of malfunctions
The peculiarity of the steering and suspension is that if some parts fail, the car continues to work. It often happens that the driver does not even notice that something is wrong with the car until the malfunction turns into a major breakdown that requires expensive repairs.
Is it possible to diagnose and fix problems yourself

Over time, any mechanism wears out, even if operated under ideal conditions. And cars every day collide with bumps, potholes, travel hundreds of kilometers off-road, etc. And first of all, suspension and steering suffer from this.
Symptoms of a malfunction include:
- extraneous noise and knocking while driving;
- reduced steering wheel sensitivity;
- vibration of the steering wheel;
- recoil to the steering wheel when driving on uneven roads;
- the car pulls to the side.
If you notice something like this while driving, it is worth checking if everything is in order with the suspension. There are also techniques that will allow even an ignorant person in cars to determine deviations from the norm in the control system and to resort to the help of a specialist in time. It is enough just to have an idea about the structure of the system. And the owner, savvy with knowledge of mechanics, can easily eliminate the problem that has arisen.
Steering - purpose and design

The steering is used to transmit a signal from the driver to the suspension system and wheels. The design features of the reactor plant depend on the dimensions, purpose and model of the machine, but, nevertheless, they are designed according to the same principle.
Any RC system consists of 4 elements:
- Steering wheel. Serves to transmit the driver's command to the steering mechanism through the column.
- Steering column. Connects the steering wheel to the steering gear and transfers the command from the first to the second. It is a shaft with articulated joints. New machine models are equipped with foldable (reduces the level of collision injuries) and length-adjustable steering columns. Also, in recent years, the speakers are equipped with electrical interlocking, which greatly complicates the theft process.
- Steering gear. It is a gearbox that transmits the driver's command to the steering gear. There are several varieties, depending on the model and brand of car. In passenger cars, the rack and pinion option is most often found.
- Steering drive. Performs the function of transferring the steering force from the steering mechanism to the wheels. Controls the steering angle and prevents the wheels from changing direction during suspension operation. The design features of the drive depend on the type of suspension.
Car suspension

Automotive suspension (or suspension system) is a link-steering mechanism that has shock-absorbing properties. The main functions of the suspension:
- Connection of wheels and continuous axles to the car frame.
- Ensuring a smooth ride by damping vehicle vibrations caused by uneven road surfaces.
- Changing the direction of the car by moving the propulsion elements regardless of the position of the body.
Design
The suspension system has 6 main components:
- Elastic elements. Their task is to accept and smooth out fluctuations from uneven road surfaces: holes, bumps, speed bumps. Elastic elements include springs, springs, pneumatic and hydropneumatic systems.
- Extinguishing elements. They perform shock-absorbing functions, that is, they smooth out and distribute shock loads on the body during movement. They can be hydraulic, pneumatic or hydropneumatic.
- Guiding elements. These include the wishbones and trailing arms. Designed to connect the car body and wheels, as well as to move the wheels relative to the body and change direction.
- Transverse stabilizer. It is a metal rod that serves to connect the suspension to the body part, as well as to fix and increase the lateral stability and balance of the car while driving.
- Rotary fists. They are mounted on the front axle and serve to distribute the loads throughout the suspension.
- Fasteners. Used to connect the suspension to the body and fasten the suspension system parts to each other. These include: bolts, silent blocks, ball joints.
The most common problems of switchgear and suspension, their identification and elimination

Most often, drivers pay attention to the condition of the car, when there are signs of a malfunction - something knocks, the car is pulled to the side and shakes even on minimal irregularities in the road surface. Before you seriously engage in repairs or take the car to service, it is worth checking if everything is really so serious.
Suspension malfunction. False alarm
- Noise while driving. First of all, you should check the condition of the fasteners. Perhaps the machine knocks because they are poorly fixed. In this case, it will be enough to tighten all loose elements.
- The car is pulled aside. Possible reasons:
- uneven / low tire pressure - check the wheels with a pressure gauge and, if this is the problem, fix the problem;
- uneven tire wear. If during inspection you are convinced that the rubber on the wheels is not equally worn, you should replace both tires with new ones.
Serious breakdowns and their elimination
Sometimes the signs of a malfunction elude the attention of the car owner. This happens if the mechanism wears out gradually - the driver also gradually gets used to changes in the operation of the system, not paying attention to the fact that the situation is getting worse.
The shock absorber is out of order
How to determine? Rocking method. That is, alternately pressing on each corner of the body. Having rocked the car well, you should see how quickly it takes its normal position. Ideally, if immediately, but one or two smooth swaying by inertia is acceptable. If the car continues to swing after you let it go, then its damping system is out of order.
Visual signs: Oil leaks on the shock absorber housing.
What to do? Remove the old shock absorber and replace it with a new one. Sometimes you can limit yourself to replacing the most worn out parts. In order to remove the shock absorbing device built into the rack, you will have to disassemble it. Removing a free-standing device does not require disassembling the suspension.
It should be noted that it is necessary to change the shock absorbers in pairs, even if only one is out of order.
Before installing a new device on the machine, bleed it:
- Install the shock absorber stem downwards.
- Squeeze gently until it stops, fixing it in this position for a few seconds.
- Turn the device over and move the stem to the initial position.
- Repeat all over again 4 times.
- After that, a check is carried out - the shock-absorbing device is installed in a fixed position with the stem up, after which an intensive but uniform compression is performed.
- Having finished pumping, in no case should the device be turned upside down with the rod.
The shock absorber is now fitted to the vehicle. All fastening and threaded structural elements are clamped with a torque wrench.
Sagging springs

How to determine? Measure the distance between the wheel and the body arch above it. In a passenger car, not loaded, 3-4 fingers, placed with an edge, are freely placed in the space between the tire and the arch. If the distance is narrower, the reason is almost always the spring sagging.
What to do? Replace springs. It should be noted that the springs are changed in pairs, both rear and / or both front. It is also imperative to change the rubber gaskets, even if the old ones have not yet worn out.
Procedure:
- Purchase a spring puller - without it, dismantling the part is impossible. Pullers are external (suitable for working with springs located in a rack) and internal (it is better to choose them to replace individual springs).
- Pullers are installed on both sides of the spring, which is then pulled together with their help when the suspension is loaded.
- Then the suspension must be unloaded and the spring removed.
- Install a new, pre-compressed spring. Attention should be paid to the position of the end coils and strippers so that access to the latter is open.
- After installing the springs, they should be checked by alternately pressing on the body on each side of the car - a correctly installed part will not squeak or knock when pressed.
Defective steering tip
How to determine? Conduct an external examination. To do this, it is best to drive the car onto an overpass or resort to using a jack.
- The details of the connection are inspected, as they are the most vulnerable. If necessary, the fasteners should be replaced or deficiencies corrected.
- The boot is inspected - if it is damaged, dirt gets on the hinge joint of the steering tip, which leads to its rapid wear.
- The backlash is checked. This will require another person who will turn the steering wheel left and right. The car owner at this time must observe the behavior of the steering tips. A working mechanism does not move along the length of the pin axis by more than 1.5 mm.
The primary signs of steering tip problems include:
- knocks and squeaks when driving on an uneven surface, as well as during braking and acceleration;
- return to the gas pedal;
- the occurrence of knocks during the turn.
What to do? Replace the part. The installation process itself is simple and it is quite possible to carry it out on your own, however, upon completion, you should definitely check the wheel alignment angles at the technical station.
Replacement process:
- Apply a penetrating lubricant to the threaded joints and leave for a short time.
- Remove the cotter pin, loosen the hinge nuts.
- Use a hammer to tap the tip finger joint.
- Disconnect the rod from the steering knuckle. Then unscrew the threaded connection in the area of adjustment of the wheel angle.
- Remove the steering end.
- Clean the installation site and threads from dirt.
- Install a new part - clamp the thread on the rod, then press the finger into the steering knuckle, clamp and lock the nut connections.
- Check if the installation was done correctly - there should be no gaps in the connection, during operation the mechanism should not come into contact with the body or other parts of the car.
Symptoms of faults

If the steering wheel stops obeying the driver, then it is possible:
- The fluid level in the hydraulic booster is lowered. It is necessary to fill the liquid to the required level.
- The steering rack mounting elements have become unusable.
- The power steering system is leaking. It is required to change the rack on the steering rack.
The steering wheel vibrates when driving at high speed:
- Wheel imbalance has occurred.
- Loose mountings on wheels. Tighten the nuts.
- Rotors damaged. It needs to be replaced.
The unevenness of the road surface is given to the steering wheel:
- Shock absorbers are worn out. It needs to be replaced.
- Bearing housings or ball joints worn out. They also need to be replaced.
It is quite possible to fix some problems and replace worn-out system elements on your own, if you are not afraid of the thought of doing it yourself. But even if you prefer to serve your "iron friend" at the service station, the ability to detect a problem will always come in handy.